Understanding Intestinal Dysbiosis and Successful Therapy Techniques
Understanding Intestinal Dysbiosis and Successful Therapy Techniques
Blog Article
The human gut hosts trillions of microorganisms, collectively referred to as gut microbiota. These microorganisms play a vital role in maintaining overall health by aiding digestion, supporting the disease fighting capability, as well as influencing mental health. However, when the balance of these microorganisms is disrupted, an ailment known as **intestinal dysbiosis** occurs. This imbalance can result in a variety of health problems, starting from mild digestive discomfort to more serious chronic conditions. In this article, we will explore the complexities, oral dysbacteriosis, and treatments for intestinal dysbiosis.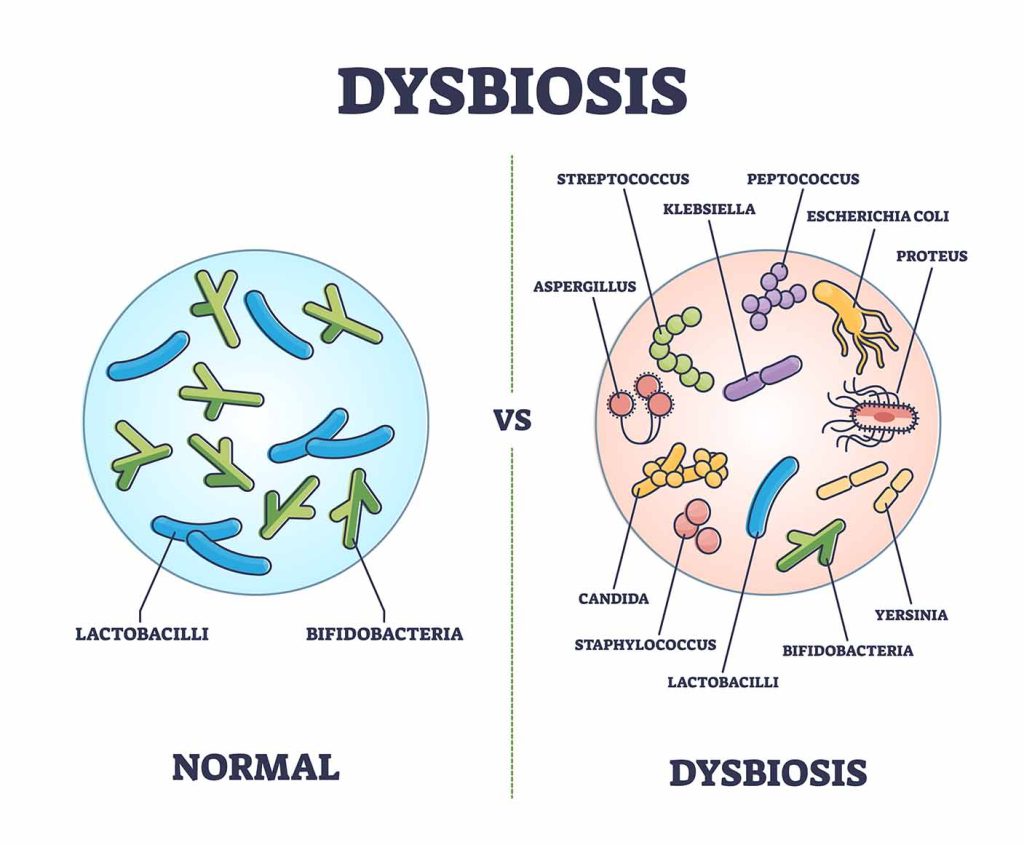
What is Intestinal Dysbiosis?
Intestinal dysbiosis describes an imbalance inside the composition with the gut microbiota, where unwanted organisms, fungi, and other pathogens outnumber the beneficial ones. This imbalance can happen from various factors, including poor diet, stress, antibiotic use, infections, or chronic illnesses. When the gut microbiota is disrupted, it might impair the gut's capacity to function properly, bringing about a range of symptoms and health problems.
Causes of Intestinal Dysbiosis
Several factors can contribute to the development of intestinal dysbiosis:
1. Antibiotic Use Antibiotics are made to kill viruses, but they can also eliminate beneficial bacteria inside the gut, disrupting the microbial balance.
2. Poor Diet A diet full of processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can promote the increase of parasites while depriving beneficial bacteria of the nutrients they should thrive.
3. Chronic Stress Stress can adjust gut motility and secretion, creating an atmosphere that favors harmful bacteria.
4. Infections Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can disrupt the gut microbiota.
5. Lifestyle Factors Lack of sleep, sedentary behavior, and excessive alcohol consumption can also give rise to dysbiosis.
6. Medical Conditions Conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and autoimmune disorders tend to be associated with gut microbiota imbalances.
Symptoms of Intestinal Dysbiosis
The symptoms of intestinal dysbiosis may differ widely according to the severity with the imbalance and the individual's all around health. Common symptoms include:
- Bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Food intolerances
- Fatigue and low energy
- Skin issues like acne or eczema
- Mood disturbances, including anxiety and depression
- Weakened disease fighting capability and frequent infections
In more serious cases, dysbiosis continues to be linked to chronic conditions including obesity, diabetes, as well as neurological disorders.
Diagnosing Intestinal Dysbiosis
Diagnosing intestinal dysbiosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. A doctor may recommend:
- Stool Analysis: This test examines the composition of the gut microbiota, identifying imbalances in bacterial populations.
- Breath Tests: These tests can detect the presence of parasites by measuring gases produced inside gut.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be used to check for markers of inflammation or nutrient deficiencies connected with dysbiosis.
Treatment Options for Intestinal Dysbiosis
The goal of treating intestinal dysbiosis is usually to restore the balance of the gut microbiota and support overall gut health. Treatment strategies might include:
1. Probiotics and Prebiotics:
- Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria which can help replenish the gut microbiota. They are found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, plus supplement form.
- Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial bacteria. Foods abundant with prebiotics include garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus.
2. Dietary Changes:
- Adopting a diet abundant in whole, unprocessed foods supports gut health. Focus on fiber-rich fruit and veggies, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Avoid foods that promote dysbiosis, including refined sugars, artificial sweeteners, and junk foods.
3. Antimicrobial Treatments:
- In cases where unwanted organisms or fungi are overgrown, healthcare providers may prescribe antimicrobial medications or a pill (e.g., oregano oil, berberine) to the pathogens.
4. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Managing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or relaxation can positively impact gut health.
- Regular exercise and adequate sleep are also essential for maintaining a healthy gut.
5. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT):
- In severe cases of dysbiosis, particularly those associated with recurrent *Clostridioides difficile* infections, FMT may be considered. This procedure involves transplanting stool from a healthy donor into the patient's gut to regenerate microbial balance.
Addressing Underlying Conditions:
- Treating underlying medical conditions, like IBD or IBS, may help resolve dysbiosis which will help prevent recurrence.
Preventing Intestinal Dysbiosis
Prevention is vital to maintaining a wholesome gut microbiota. Here are some tips to lessen the risk of dysbiosis:
- Use antibiotics only if necessary and follow your healthcare provider's instructions.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fiber and fermented foods.
- Stay hydrated and limit alcohol consumption.
- Manage stress through mindfulness and relaxation techniques.
- Get routine workouts and prioritize sleep.
Intestinal dysbiosis is a kind of yet often overlooked condition that may have far-reaching effects on health. By understanding the causes and signs and symptoms of dysbiosis, individuals will take proactive steps to bring back and maintain a normal gut microbiota. Through a mix of dietary changes, probiotics, lifestyle modifications, and treatments, it is possible to achieve a balanced gut and improve overall well-being. If you suspect you might have intestinal dysbiosis, consult a health care professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment solution.
Taking care of your gut is not only just about digestion—it's about nurturing the inspiration of your health.